4 min read
Why the Human Factor is Critical to Successful Medical Imaging, Part 2: Human-Centric Design Considerations
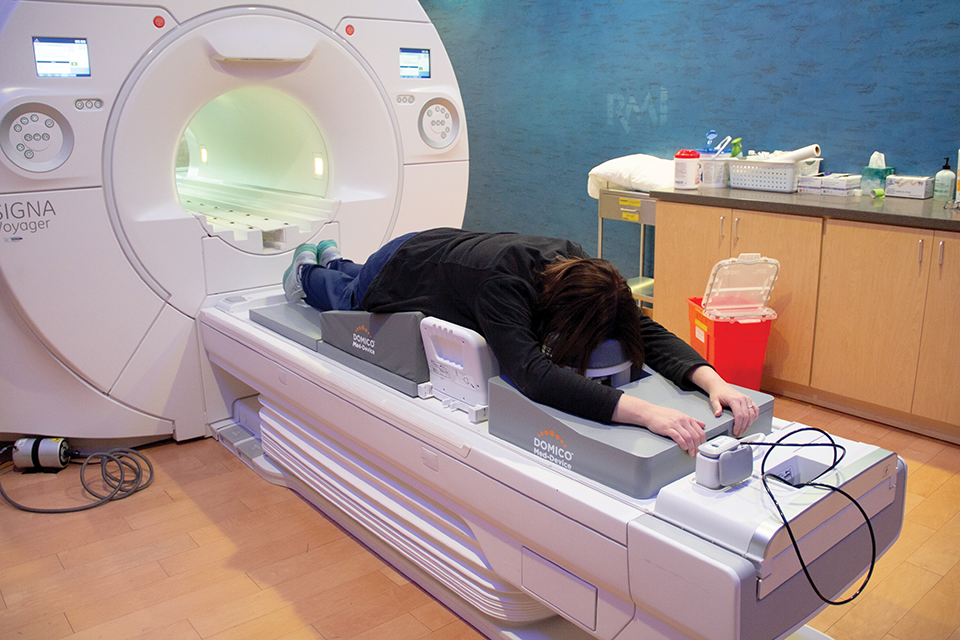
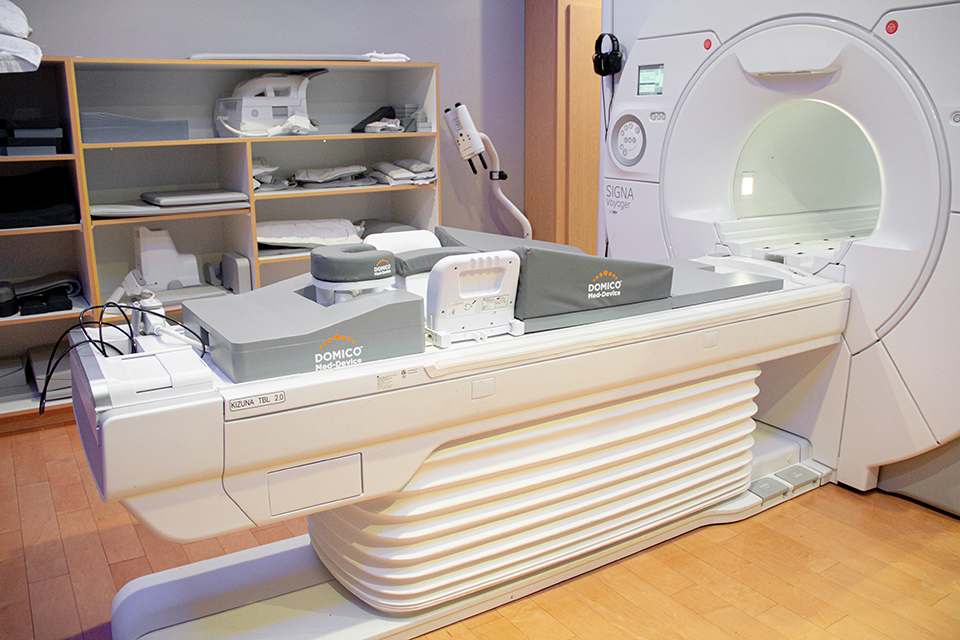
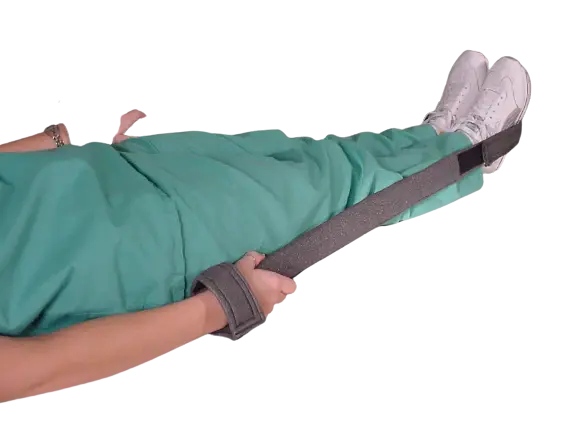
This is Part 2 of a 3-part series on how human-centric design fosters medical imaging success. Part 1detailed how overlooking the human factor...