A Complete Guide to Choosing Table Pads for your Healthcare Facility
When it comes to ensuring patient comfort and enhancing the effectiveness of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, selecting the right table pad is...
4 min read
Domico Med-Device Updated on December 2, 2024
In medical settings, the use of straps is critical for ensuring patient safety and comfort. Each type of strap serves a unique purpose and offers distinct benefits, making it vital to choose the right one for specific clinical scenarios. This guide will explore these straps in detail, helping you make informed decisions about which to use and why.
 1. Chin Straps
1. Chin StrapsChin straps are designed to secure a patient’s head and jaw, providing crucial support during various medical procedures. These straps are particularly important in settings where maintaining precise head positioning is necessary for successful outcomes.
Enhanced Stability: Chin straps keep the head in a fixed position, which is essential for procedures requiring high precision, such as in radiology or certain types of surgery.
Patient Comfort: Made from soft materials, chin straps are designed to minimize discomfort during use, even over extended periods.
Custom Fit: Many chin straps feature adjustable components, allowing them to be tailored to fit different head sizes and shapes.
Imaging Procedures: In CT scans and MRIs, accurate head alignment is critical for obtaining clear images. Chin straps help prevent movement that could blur the results.
Dental Procedures: For dental surgeries and treatments requiring specific head positioning, chin straps ensure that the patient remains still and in the desired position.
Neurosurgery: In procedures involving the brain or spine, maintaining head stability is crucial for both patient safety and procedural accuracy.
 2. Security Straps
2. Security StrapsSecurity Straps are versatile devices used to secure patients to beds or tables. They are designed to prevent accidental movement, which could jeopardize the success of various medical procedures.
Increased Safety: By securing patients in place, restraint belts reduce the risk of falls or unwanted movement, which is particularly important during surgeries or diagnostic tests.
Adaptability: Security Straps can be used across different medical environments, from emergency rooms to routine surgical suites.
Ease of Application: Typically equipped with simple fastening mechanisms, restraint belts can be quickly applied and adjusted.
Surgical Settings: In operating rooms, security straps keep patients from moving, ensuring that surgical procedures are conducted safely and effectively.
Emergency Care: During emergencies, security straps help immobilize patients to prevent further injury and facilitate necessary interventions.
Diagnostic Imaging: For procedures like X-rays or MRIs, restraint belts can help position patients correctly and prevent movement that could compromise image quality.
 3. EZ-Straps
3. EZ-StrapsEZ-Straps are designed for rapid application and adjustment, combining the convenience of quick use with effective patient stabilization. These modern straps are particularly beneficial in fast-paced medical environments.
Speed and Efficiency: EZ-Straps are easy to apply and adjust, making them ideal for situations where time is of the essence, such as in emergency care.
High Durability: Constructed from robust materials, EZ-Straps are built to endure frequent use and cleaning.
Versatility: They are suitable for a wide range of applications, including surgical procedures, imaging, and emergency scenarios.
Emergency Rooms: EZ-Straps allow for quick stabilization of patients, which is critical in emergencies where every second counts.
Busy Surgical Suites: The ease of use of EZ-Straps helps streamline preparations and adjustments during complex surgeries.
Diagnostic Imaging: Their versatility makes EZ-Straps suitable for various imaging modalities, providing secure positioning with minimal hassle.
The choice of material affects both patient comfort and safety. Straps should be made from soft, non-irritating materials to avoid discomfort or skin damage. For instance, chin straps should have a soft inner lining to prevent irritation, while restraint belts should be designed to minimize pressure points.
Adjustable straps ensure a secure fit across different body sizes and shapes. This is particularly important for straps like chin straps and restraint belts, which need to accommodate a wide range of patients.
In high-pressure environments, ease of use is crucial. Look for straps that are straightforward to apply and adjust. EZ-Straps, for example, are designed for rapid application, which can be a significant advantage in fast-paced medical settings.
Durability is essential for straps that undergo frequent use. Opt for straps made from high-quality, durable materials that can withstand regular cleaning and handling without losing their effectiveness.
Ensure that the straps have appropriate safety features, such as quick-release mechanisms for EZ-Straps and secure fastenings for restraint belts. These features allow for swift removal if needed, enhancing overall patient safety.
 Best Practices for Using Patient Straps
Best Practices for Using Patient StrapsFollow the manufacturer’s instructions for applying straps to ensure they are used correctly. Incorrect application can lead to discomfort or compromised safety.
Conduct routine inspections of straps to check for signs of wear and tear. Replace any damaged straps to maintain their effectiveness and safety.
Inform patients about the use of straps and address any concerns they may have. Clear communication can help reduce anxiety and ensure cooperation during procedures.
Provide training for healthcare staff on the proper use of straps. Well-trained staff are more likely to apply straps correctly and ensure patient safety.
Maintain hygiene by regularly cleaning and disinfecting straps according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Proper maintenance helps prevent the spread of infections and ensures the longevity of the straps.
Regularly assess the effectiveness of the straps in meeting clinical needs. Gather feedback from staff and patients to identify any issues and make necessary improvements.
As medical technology evolves, ensure that the straps you use are compatible with new equipment and procedures. For example, some imaging systems may require specific types of straps to avoid interference with the technology.
Different patients may have specific needs based on their condition or treatment. Take these into account when selecting and using straps to ensure they provide the necessary support without causing additional discomfort.
Choosing the right straps—whether chin straps, restraint belts, or EZ-Straps—is crucial for ensuring patient safety, comfort, and procedural success. By understanding the benefits and applications of each type of strap and considering factors such as material, adjustability, and ease of use, you can make informed decisions that enhance patient care. Prioritizing comfort, durability, and functionality will help you provide a better experience for your patients, ultimately contributing to improved outcomes and higher satisfaction levels.
Incorporating these best practices into your patient care protocols will not only ensure that you are using the best tools available but also help you maintain a high standard of care in your medical facility. Whether you're working in a surgical suite, emergency room, or diagnostic imaging center, the right straps will make a significant difference in both patient safety and procedural efficiency.
Want to learn more? Check out these blogs to read more about patient immobilization:
When it comes to ensuring patient comfort and enhancing the effectiveness of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, selecting the right table pad is...

Medical sewing plays a vital role in the healthcare industry, involving the meticulous design and production of essential medical textiles and...
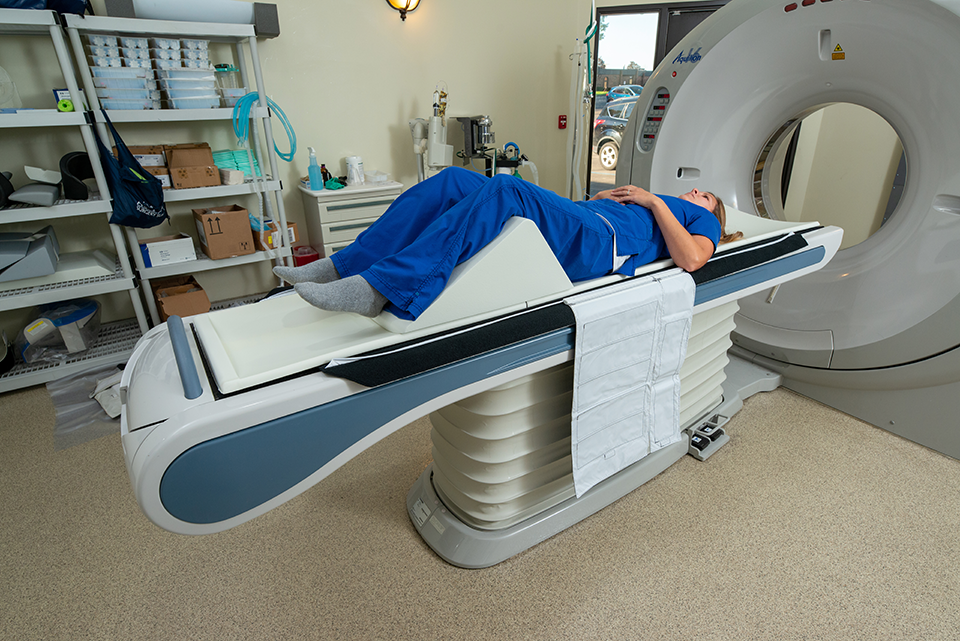
This is Part 2 of a 3-part series on patient positioning factors that improve imaging and therapy success. Part 1discussed how patient positioning...