How to Eliminate Cord Chaos & Contamination in the OR, Part 1: Safety Risks of Poor Cord Management
This is Part 1 in a 3-part series on strategic cord management in the operating room. In Part 1, we’ll offer an overview of the safety risks of...
4 min read
Domico Med-Device Updated on December 2, 2024
Discover the financial implications of apparatus replacement when they fall below the sterile field.
Maintaining a sterile field is crucial in the operating room to prevent infections, ensure patient safety, and minimize cost. It is essential for surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to adhere to strict protocols and guidelines to maintain the sterility of the operating environment.
When an apparatus falls below the sterile field during surgery, it can compromise the integrity of the sterile environment. This can have serious consequences for patient safety, as it introduces the risk of infection and other complications. A sterile apparatus that comes into contact with non-sterile surfaces can introduce harmful bacteria or pathogens into the surgical site, increasing the chances of post-operative infections.
Along with patient safety, falling apparatuses can be costly. Tool replacement cost per procedure is $55.60, with an estimated annual cost based on frequency of fall is $154,090**. That’s on top of the already expensive Operating Room Time of $46.04 per minute*.
Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to be vigilant and take immediate action if an apparatus falls below the sterile field. This may involve replacing the contaminated apparatus to ensure the sterility of the surgical environment and prevent any potential harm to the patient.
When an apparatus falls below the sterile field during surgery, it can have a significant impact on patient safety. As mentioned earlier, the introduction of non-sterile apparatus into the surgical site increases the risk of infections. Surgical site infections (SSIs) are a common complication of surgery and can lead to prolonged hospital stays, increased healthcare costs, and even patient mortality.
In addition to SSIs, apparatus falling below the sterile field can also increase the risk of other complications such as sepsis, abscess formation, and wound dehiscence. These complications not only affect patient outcomes but also add to the financial burden on healthcare institutions.
Furthermore, when an apparatus falls below the sterile field, it may require additional time and resources to address the issue. This can disrupt the workflow in the operating room, potentially leading to delays in the surgery, prolonged anesthesia exposure time for the patient, and increased operating room costs. Therefore, preventing apparatus from falling below the sterile field is crucial to maintain patient safety and minimize the financial implications associated with apparatus replacement.
Apparatus replacement due to falling below the sterile field can have significant financial implications for healthcare institutions. The cost of replacing apparatus can vary depending on the type and complexity of the equipment. In some cases, the apparatus may need to be discarded and replaced with a new one, while in other cases, it may be possible to sterilize and reuse the apparatus.
Apart from the direct cost of apparatus replacement, there are also indirect costs associated with the process. These include the cost of the time and effort required to identify and replace the contaminated apparatus, and the potential impact on the surgical schedule and operating room utilization.
Moreover, apparatus replacement can also lead to increased healthcare-associated costs, such as prolonged hospital stays, additional diagnostic tests, and the need for post-operative care. These costs can further add to the financial burden on healthcare institutions, especially in cases where patients develop complications as a result of the contaminated apparatus.
Overall, the financial consequences of apparatus replacement due to falling below the sterile field should not be underestimated. It is crucial for healthcare institutions to implement strategies to minimize these costs and ensure the efficient management of surgical equipment.
Several factors can influence the cost of apparatus replacement when they fall below the sterile field. One of the major factors is the type and complexity of the apparatus. More sophisticated and specialized equipment may be more expensive to replace compared to simpler instruments.
The frequency of apparatus replacement can also impact the overall cost. If apparatus falling below the sterile field is a recurring issue, the cumulative cost of replacement can be significant over time. Therefore, it is important to address the underlying causes of apparatus falling below the sterile field and implement measures to prevent such incidents from occurring.
Additionally, the availability of spare apparatus and the efficiency of the apparatus replacement process can also affect the cost. If spare apparatus is readily available and the replacement process is streamlined, it can help minimize the financial burden.
Lastly, the overall budget and financial resources of the healthcare institution can also influence the cost of apparatus replacement. Institutions with limited resources may face greater challenges in managing the financial implications of apparatus replacement.
To minimize the cost of apparatus replacement when they fall below the sterile field, healthcare institutions can implement several strategies. One of the key strategies is the proper education and training of healthcare professionals involved in surgical procedures. By ensuring that all staff members understand the importance of maintaining a sterile field and are aware of the potential consequences of apparatus falling below the sterile field, the likelihood of such incidents can be reduced.
Regular audits and inspections of the operating room can also help identify any potential issues that may lead to apparatus falling below the sterile field. By addressing these issues proactively, healthcare institutions can prevent accidents and minimize the need for apparatus replacement.
Furthermore, implementing strict protocols and guidelines for the handling and placement of apparatus in the operating room can help reduce the risk of apparatus falling below the sterile field. This may include using specialized trays or holders for apparatus, ensuring proper labeling and organization of surgical equipment, and conducting regular checks during surgical procedures to ensure the apparatus remains within the sterile field.
Collaboration between healthcare professionals, including surgeons, nurses, and sterilization technicians, is also crucial in minimizing apparatus replacement costs. By establishing clear communication channels and fostering a culture of teamwork and accountability, healthcare institutions can improve the overall management of surgical equipment and reduce the likelihood of apparatus falling below the sterile field.
In conclusion, the cost of apparatus replacement when they fall below the sterile field during surgery in the operating room can have significant financial implications for healthcare institutions. By understanding the importance of maintaining a sterile field, addressing the factors that contribute to apparatus falling below the sterile field, and implementing strategies to minimize replacement costs, healthcare institutions can ensure patient safety and optimize their financial resources.
* Cost of Operating Room Time is $46.04 per Minute https://www.researchgate.net/publication/364098813_Cost_of_OR_Time_is_4604_per_Minute
** Accidentally falling instruments during orthopedic surgery: Time to wake up! https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18844911/
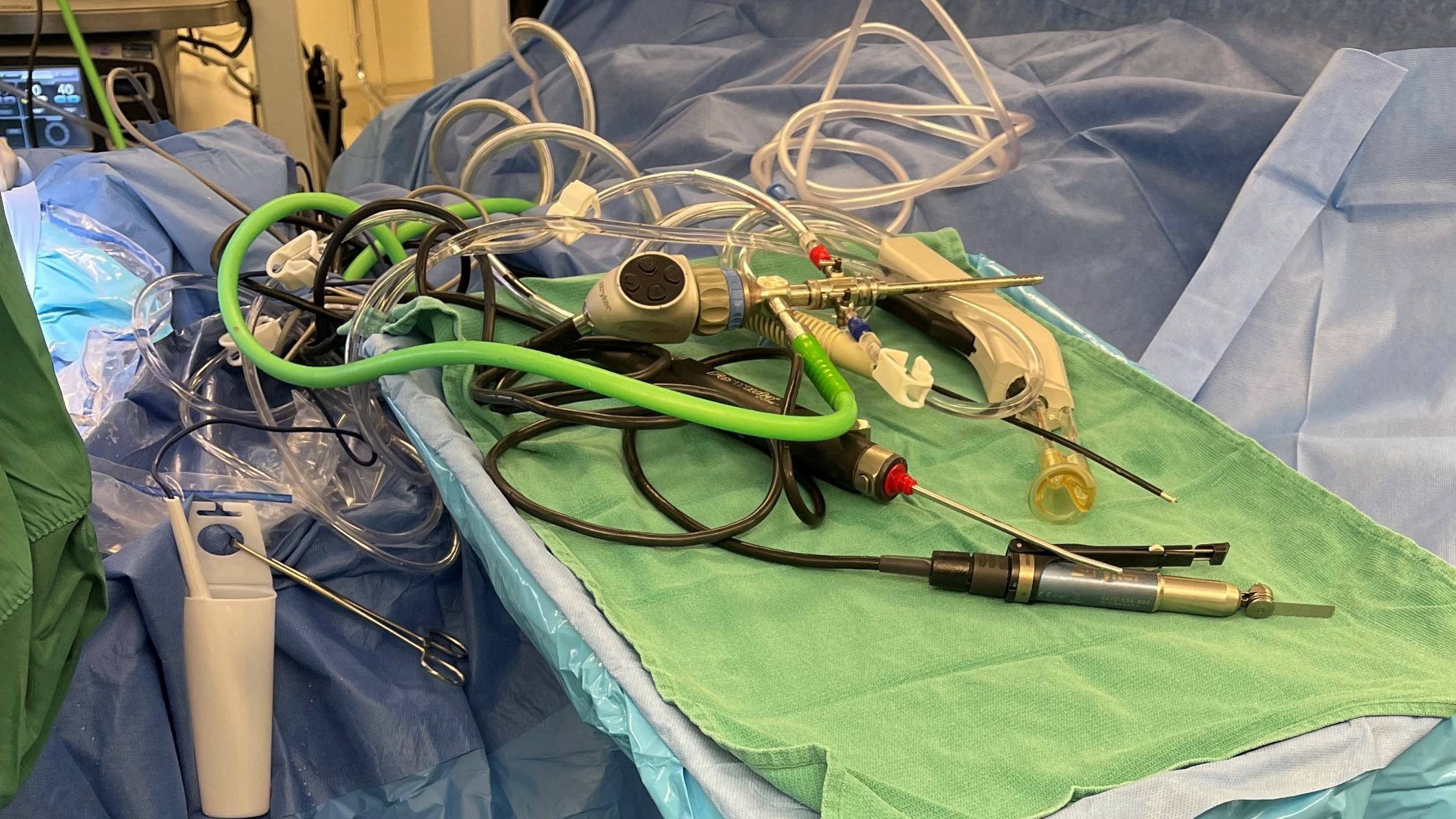
This is Part 1 in a 3-part series on strategic cord management in the operating room. In Part 1, we’ll offer an overview of the safety risks of...
Surgical table padsare indispensable in the operating room, functioning not only as a supportive surface for patients but also as a crucial element...

Operating room table pads play a vital role in the surgical suite, offering patients a secure and comfortable surface during procedures. These pads...