A Comprehensive Guide to Pediatric Patient Positioning in Diagnostic Imaging
Discover essential techniques and considerations for optimizing pediatric patient positioning to enhance diagnostic accuracy and patient comfort in...
5 min read
Domico Med-Device Updated on December 2, 2024
Accurate diagnostic imaging is the cornerstone of modern healthcare, playing a crucial role in the timely and precise diagnosis of various medical conditions. Whether it's identifying a fracture, detecting a tumor, or monitoring a chronic condition, high-quality imaging is indispensable. Among the many factors that contribute to the quality of diagnostic imaging, optimal patient positioning stands out as one of the most critical. This seemingly simple aspect of radiological practice directly influences image quality, diagnostic accuracy, patient safety, and overall patient well-being.
Radiological examinations, including X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, are indispensable tools in diagnosing and monitoring medical conditions. Achieving high-quality images is essential not only for accurate diagnosis but also for effective treatment planning and comprehensive patient management. Optimal patient positioning is a fundamental aspect of this process. It directly affects image quality, proper anatomical visualization, and the ability to detect pathology. Inadequate positioning can lead to pathological misinterpretation, unnecessary additional imaging procedures, loss of revenue, patient anxiety, unnecessary pain, and increased radiation exposure. Therefore, understanding and implementing precise patient positioning techniques is crucial for radiology departments aiming to provide exceptional patient care and diagnostic accuracy.
Patient positioning in radiology is not merely about placing a patient on the imaging table. It involves a careful and strategic approach to ensure that the anatomical area of interest is appropriately visualized, free from distortions or artifacts that could hinder an accurate diagnosis. The success of radiological examinations largely depends on how well the patient is positioned during the imaging process.
Inadequate patient positioning can have far-reaching consequences. It can lead to misinterpretation of images, resulting in incorrect diagnoses that could affect patient outcomes. Furthermore, poor positioning often necessitates repeat imaging, which not only increases healthcare costs but also exposes patients to additional radiation, posing significant health risks. Additionally, suboptimal positioning can cause discomfort or pain for the patient, leading to increased anxiety and a negative experience with the healthcare system.
Achieving optimal patient positioning in radiology is not without its challenges. These challenges can vary significantly depending on the patient's physical condition, emotional state, and the specific imaging modality being used.
1. Patient Physical Condition and Emotional State:
Patients undergoing radiological examinations are often dealing with various physical and emotional challenges. They may be in pain, anxious about their diagnosis, or fearful of the unknown aspects of the imaging procedure. For instance, patients who are about to undergo an MRI may experience heightened anxiety due to the enclosed nature of the machine, leading to claustrophobia. These emotional and physical states can make it difficult to achieve the ideal positioning for imaging.
2. Anatomical Complexity and Imaging Modality:
Different body parts require specific positioning to ensure clear and accurate visualization. For example, imaging the spine requires precise alignment to capture all relevant anatomical details while avoiding unnecessary exposure to radiation in adjacent areas. Similarly, imaging joints or complex structures like the brain necessitates careful positioning to reduce artifacts and improve image quality. Each imaging  modality, whether it's MRI, CT, or X-ray, presents unique challenges in positioning due to the varying requirements for optimal image acquisition.
modality, whether it's MRI, CT, or X-ray, presents unique challenges in positioning due to the varying requirements for optimal image acquisition.
3. Need for External Support:
Textbook patient positions are often idealized and may not be achievable in real-world scenarios without additional support. The use of pads, pillows, and cushions is essential to ensure that patients are comfortably and correctly positioned on the imaging table. These supports play a crucial role in reducing pressure points, minimizing patient discomfort, and allowing for the precise positioning required for high-quality imaging.
The benefits of optimal patient positioning in radiology extend beyond just image quality. They encompass patient safety, radiation dose optimization, workflow efficiency, and overall patient satisfaction.
1. Enhanced Image Quality:
One of the primary benefits of correct patient positioning is its direct impact on image quality. Proper alignment and stabilization of the patient's body part under examination ensure optimal visualization, reducing artifacts and distortions that may hinder accurate diagnosis. High-quality images lead to more precise evaluations, better-informed clinical decisions, and improved patient treatment outcomes. Additionally, patients who are comfortably positioned are more likely to remain still during the imaging procedure, further enhancing image clarity and reducing the need for repeat scans.
the patient's body part under examination ensure optimal visualization, reducing artifacts and distortions that may hinder accurate diagnosis. High-quality images lead to more precise evaluations, better-informed clinical decisions, and improved patient treatment outcomes. Additionally, patients who are comfortably positioned are more likely to remain still during the imaging procedure, further enhancing image clarity and reducing the need for repeat scans.
2. Radiation Safety:
Optimal patient positioning also plays a vital role in radiation dose optimization, particularly in modalities like CT and X-ray that involve ionizing radiation. Correct positioning allows for accurate collimation, minimizing the radiation field to the area of interest and reducing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues, vital organs, and adjacent structures. By adhering to appropriate positioning protocols, radiographers can maintain image quality while limiting radiation dose, safeguarding patient health and well-being.
3. Workflow Efficiency and Consistency:
Good positioning adjuncts, such as pads and cushions, are key to standardizing positioning protocols and ensuring consistency across radiology departments. Consistent patient positioning is crucial for achieving reliable and reproducible imaging results. Establishing standardized positioning protocols helps minimize variations in practice, ensuring that all patients receive the same high standard of care, regardless of the technologist performing the procedure. Additionally, technologist training and continuing education are essential components of this effort, equipping radiographers with the skills, knowledge, and tools needed to accurately position patients and adapt to diverse clinical scenarios.
At Domico Med-Device, we understand the importance of patient comfort and stability in achieving successful MRI procedures. That's why we offer a range of positioning aids designed specifically for use in MRI environments. Our products are engineered with patient comfort, durability, and minimal attenuation in mind, making them ideal for use in various MRI applications.
![VMR38X01 [MedVac Immobilizer Child] _1](https://www.domicomed.com/hs-fs/hubfs/VMR38X01%20%5BMedVac%20Immobilizer%20Child%5D%20_1.png?width=375&height=251&name=VMR38X01%20%5BMedVac%20Immobilizer%20Child%5D%20_1.png) 1. MedVac Immobilizer
1. MedVac ImmobilizerThe MedVac Immobilizer is an innovative solution for immobilizing patients during MRI scans, particularly pediatric patients. This flexible splint becomes rigid when vacuumed, providing excellent stability and preventing movement during the scan. The MedVac Immobilizer is designed to be comfortable for the patient while ensuring that they remain in the correct position throughout the procedure. By reducing the likelihood of movement artifacts, this system helps produce clearer images and improves the overall success of the MRI scan.
 2. Knee Wedge
2. Knee WedgeOur knee wedge is a simple yet effective positioning aid that can significantly enhance patient comfort during MRI procedures. By placing the wedge under the patient's knees, pressure on the lower back is relieved, allowing the patient to remain comfortable and still for the duration of the scan. The knee wedge is particularly beneficial for patients with lower back pain or discomfort, as it helps prevent involuntary movements that could compromise the quality of the images.
 3. Leg Rest with Knee Cutouts
3. Leg Rest with Knee CutoutsThe Leg Rest with Knee Cutouts is another valuable positioning aid that supports the patient's legs during the MRI scan. By elevating the legs and providing support, the leg rest helps maintain proper alignment and reduces the risk of discomfort. This positioning aid is ideal for patients who may struggle to remain in a flat position on the MRI table, ensuring that they remain comfortable and still throughout the procedure.
In conclusion, optimal patient positioning is an indispensable component of radiological practice, exerting a profound influence on image quality, diagnostic accuracy, and radiation dose optimization. Perfect positioning is often a challenging but essential component of the scanning activity, as patients are often in pain, confused, anxious, or simply uncomfortable. This is where the correct use of pads and cushions plays a vital role in accommodating patients by mitigating their pains, anxieties, and fears. By implementing standardized positioning protocols, investing in proper padding and technologist training, and prioritizing patient education, radiology departments can elevate the quality of diagnostic imaging, reduce unnecessary repeated images, and ultimately enhance patient care. A commitment to precise patient positioning underscores the dedication of radiology professionals to delivering accurate diagnoses and optimal healthcare outcomes.
Optimal patient positioning is not just a technical requirement; it's a critical aspect of patient-centered care in radiology. By focusing on the details of positioning, radiology professionals contribute to better healthcare outcomes, ensuring that every image captured is of the highest possible quality and every patient receives the best possible care.
Want to learn more? Check out these blog to learn more about the importance of patient positioning in radiology:
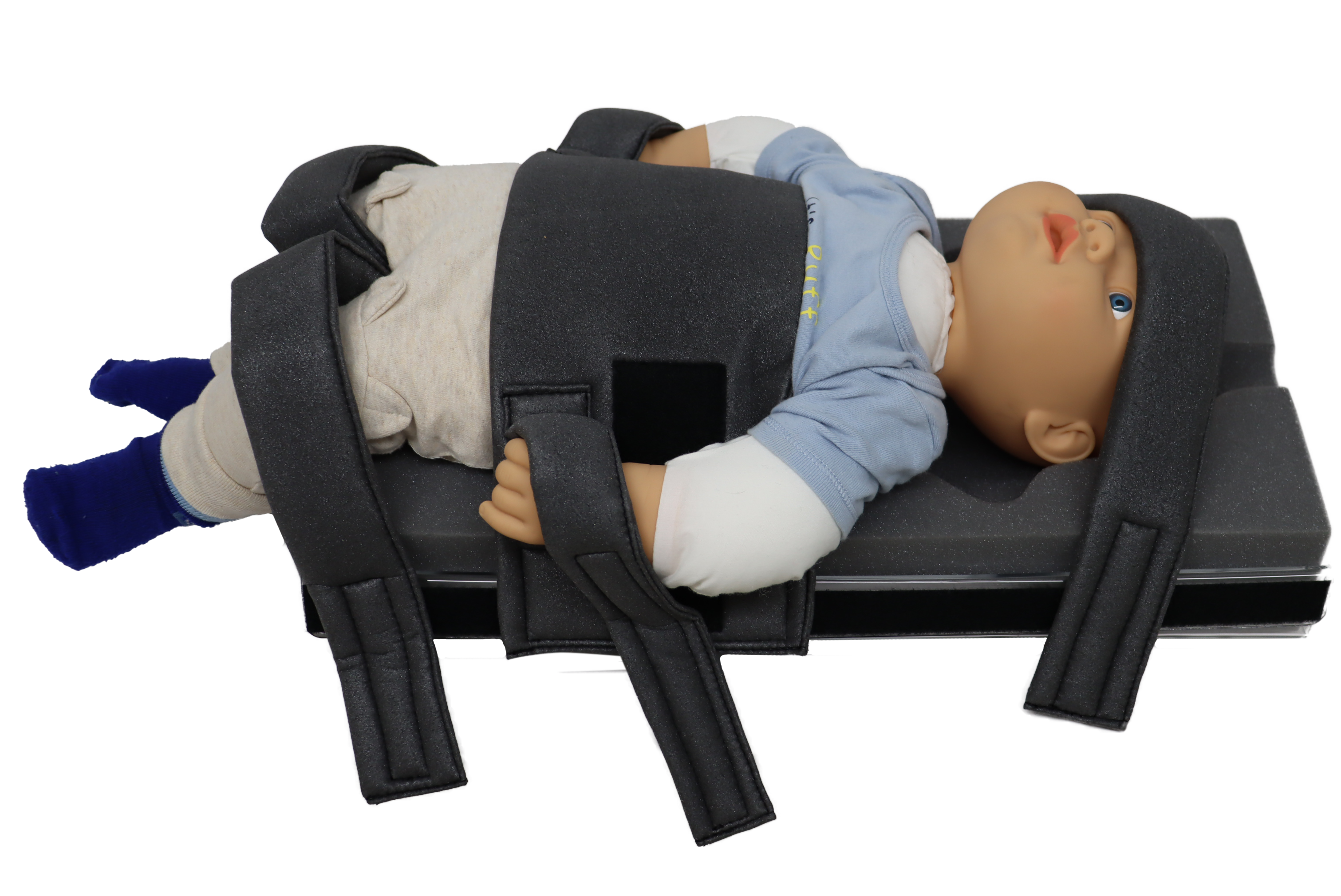
Discover essential techniques and considerations for optimizing pediatric patient positioning to enhance diagnostic accuracy and patient comfort in...
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a crucial diagnostic tool that offers unparalleled imaging capabilities, enabling healthcare professionals to...
In a high-stakes environment like the operating room (OR), every detail contributes to the success of surgical procedures and patient care. From...